Bipolar Transistors - BJT
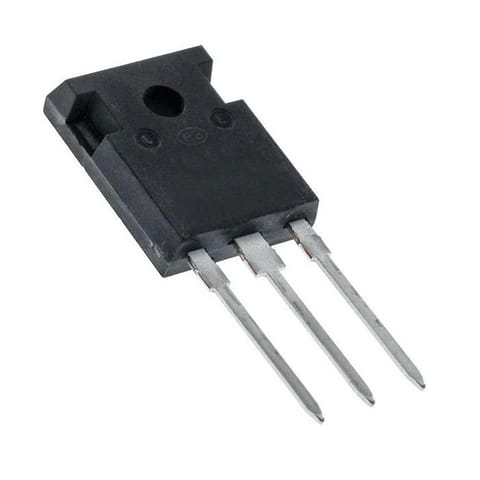
Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) are semiconductor devices used for amplification and switching applications. They consist of three layers—emitter, base, and collector—and operate by controlling current flow between the collector and emitter using a small base current. BJTs are classified into NPN and PNP types, with NPN being more commonly used in electronic circuits. They are widely utilized in amplifiers, oscillators, and switching regulators due to their high current gain and fast response. BJTs play a crucial role in consumer electronics, power management, and industrial automation systems.
Showing 25 of 163 products